Plasma Proteins & Their Functions Details
Plasma Protein. There are 4 Plasma Proteins. The proteins that are present in blood are called plasma proteins. Plasma proteins are Albumin, Globulin, Fibrinogen, and Prothombin.
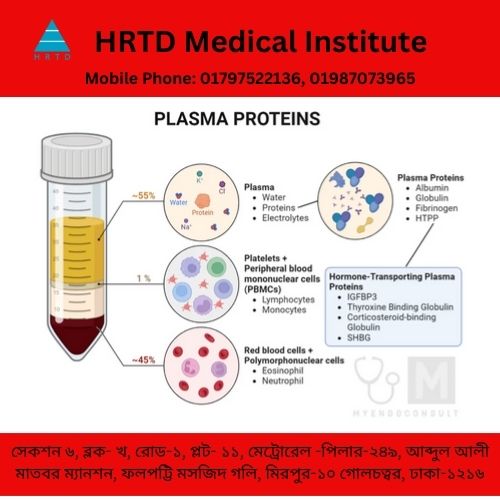
To know details about Plasma Proteins, there are some medical courses at HRTD Medical Institute. These Courses are Paramedical, Paramedical Vet, Diploma Medical Assistant in Veterinary that is DMA Vet, Diploma in Medicine & Surgery, DMS Vet, DMDS, DMDS Vet, Pathology Course, etc.
Define Albumin
Albumin is a simple protein present both in animal and plant physiological fluids and tissue.
Functions of Albumin
It plays many important roles including
- Maintenance of appropriate osmotic pressure
- Binding and transport of various substances like hormones, and drugs in the blood.
- Neutralization of free radicals.
Define Globulin
Glubulin area group of proteins in our blood.They are made in our immune system.
Functions of Globulin
- Liver function
- Blood clotting
- Fighting infection
Classification of Globulin
There are 3types of globulins
- Alpha globulin
- Beta globulin
- Gamma globulin
Fibrinogen
Fibrinogen is a blood-clotting protein produced in the liver.
Functions
- It responds to injury, infection, and inflammation.
- Wounding healing
- Growing new blood vessels.
- A balance of fibrinogen and its breakdown product fibrin helps us get rid of unneeded blood vessels.
Prothrombin
Prothrombin is a protein made by the liver
Functions of prothrombin
- prothrombin helps blood to clot
Prothrombin Time
The prothrombin time is one way of measuring how long it takes blood to form a clot, and it is measuring how long it takes blood to form a clot, and it is measured in seconds. A normal pt indicates that a normal amount of blood-clotting protein is available.
Blood clotting
Otherwise known as blood clotting, coagulation plays a pivotal role in the repair of blood vessels. The heart pumps blood throughout the body with the aid of the arteries, and in turn, blood goes back to the heart through the veins. When the blood vessels become injured, it will trigger the blood clotting process This way, the body will repair the damage to stop hemorrhage or bleeding from happening.
For instance, the damage happens in the lining of the blood vessels, and the platelets will form an initial plug on the affected area They will initiate the clotting process with the aid of certain clotting factors produced in the body Clogged arteries and atherosclerosis disease medical concept with a three-dimensional human artery with blood cells that is blocked by plaque buildup of cholesterol as a symbol of vascular diseases Image Credit Lightspring/Shutterstock
Clotting Factors
Clotting factors are components found in plasma that are linked to the blood clotting process. These factors are named and numbered based on their discovery Though there are a total of 13 numerals, there are only 2 clotting factors Factor VI was discovered to be part of another factor
The clotting factors are:
Factor! (fibrinogen). Factor II (prothrombin).
Factor III (tissue thromboplastin or tissue factor).
Factor IV (ionized calcium),
Factor V (labile factor or proaccelerin).
Factor Vil (stable factor or proconvertin), and
Factor Vill (antihemophilic factor) . Additionally, the coagulation factors also include Factor IX (plasma thromboplastin component or the Christmas factor)
Factor X (Stuart-Prower factor)
Factor XI (plasma thromboplastin antecedent)
Factor XII (Hageman factor) and
Factor XIII (fibrin-stabilizing factor)
The liver uses vitamin K to produce some of the factors such as Factors I VII, IX, and X Normally, vitamin K can be consumed through the diet from plant and animal sources The normal flora of the intestine also produces vitamin K
Blood Clotting Process
Hemostasis is a way for the body to stop injured blood vessels from bleeding One of the most important parts of hemostasis is the clotting of the blood Subsequently the body needs to control the mechanisms to control and limit clotting These include dissolving excess clots that are not needed anymore. When there is an abnormality in any part of the system that controls bleeding, it can lead to hemorrhage or excessive clotting These are potentially life-threatening
Too much clotting can lead to stroke and heart attacks because blood clots can travel and clog the vessels. On the other hand, poor clotting can lead to severe blood loss even with just a slight injury to the blood vessels
Hemostasis has three major processes namely the constriction of blood vessels activity of the platelets, and activity of the proteins found in blood (clotting factors)
Injury
The first phase of the blood clotting process is injury or when a blood vessel becomes damaged This can be in the form of a small tear in the blood vessel wall that may lead to bleeding
Blood Vessel Constriction
The body will constrict the blood vessels to control blood loss. It will limit the blood flow to the affected area
Platelet Plug
In response to the injury, the body activates platelets. At the same time, chemical signals are released from small sacs in the platelets to attract other cells to the area They make a platelet plug by forming a clump together A protein called the von Willebrand factor (WWF) helps the platelets to stick together
Fibrin Clot
When a blood vessel becomes injured, the coagulation factors or clotting factors in the blood are activated. The clotting factor proteins stimulate the production of fibrin, which is a strong and strand-like substance that forms a fibrin clot For days or weeks, this fibrin clot strengthens and then dissolves when the injured blood vessel walls close and heal
Blood clotting is a crucial process that can help prevent blood loss due to injury. If there is an abnormality in any part of the process it can lead to dangerous complications such as severe blood loss. Commonly people with clotting disorders are closely monitored to prevent injuries and bleeding
 Veterinary Training Course in Dhaka Pharmacy, Dental, Nursing, Veterinary, Physiotherapy, Pathology and Homeopathy training course
Veterinary Training Course in Dhaka Pharmacy, Dental, Nursing, Veterinary, Physiotherapy, Pathology and Homeopathy training course